
In the shadow of the world’s highest peaks, a different kind of movement is taking place. Nepal, a nation of about 30 million nestled between India and China, is witnessing an unprecedented departure of its youth. This trend is reshaping the country’s future in ways both profound and concerning.
The Scale of the Exodus
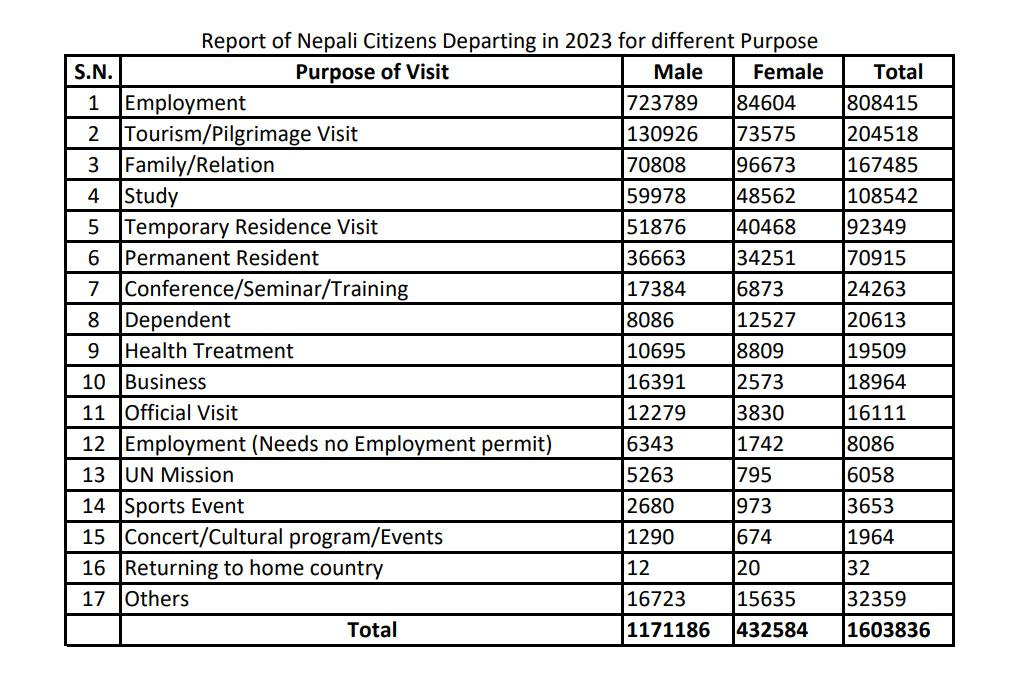
Recent data from the Department of Immigration tells a striking story:
- In 2023 alone, nearly 1.6 million Nepalese left the country
- About 71,000 departed for permanent settlement abroad
- Over 100,000 individuals are leaving monthly
- An overwhelming 95% of those leaving are young adults
These aren’t just numbers on a page. Each represents a personal story, a difficult decision, and often, a family left behind.
Why Are They Leaving?
The reasons behind this mass migration are complex, but they often boil down to a few key factors:
- Limited Job Opportunities: With an economy still heavily reliant on agriculture, many educated youth struggle to find work that matches their skills and aspirations.
- Political Instability: Years of political turmoil have led to slow economic growth and policy uncertainties.
- Better Prospects Abroad: Many young Nepalese see opportunities for higher education and better-paying jobs in countries like US, Canada, Australia, the Gulf states, Japan, South Korea, and many more.
- Social Pressures: There’s often a perception that those who go abroad are more successful, creating a cycle of aspiration and migration.
The Impact on Nepal
- Brain Drain: Nepal is losing its most educated and skilled young people, potentially hampering long-term development.
- Changing Demographics: Rural areas, in particular, are seeing a significant shift in population, with many villages now primarily inhabited by the elderly and very young.
- Economic Shifts: While remittances provide a significant boost to Nepal’s economy, the loss of young workers affects various sectors, from agriculture to emerging industries.
- Familial and Social Bonds: The migration trend has given rise to elderly care centers in urban areas, as many young people leave their parents behind. This shift challenges traditional family structures and social norms.
The Paradox of Progress
Interestingly, the visible signs of development in Nepal can be misleading. Many urban areas boast large houses and paved roads, often built with remittance money. However, these improvements mask deeper economic issues:
- Many of these newly constructed houses stand empty for much of the year.
- Capital is tied up in non-productive assets, reducing economic circulation.
- The construction boom hasn’t necessarily translated into sustainable job creation.
This situation creates a visually misleading picture of progress, while the underlying economic challenges persist.
Comparing: Nepal’s Neighbors Face Similar Challenges
Nepal isn’t alone in grappling with youth migration. Other South Asian countries like Bangladesh and Sri Lanka have faced similar issues. However, they’ve implemented some interesting strategies:
- Bangladesh has created special economic zones to attract investment from its overseas citizens.
- Sri Lanka has established programs to facilitate knowledge transfer from skilled expatriates.
Silver Linings: The Positive Side of Migration
While the exodus presents significant challenges, it’s not without some benefits:
- Remittances: Money sent home by Nepalese working abroad accounted for 25% of the country’s GDP. This influx of foreign currency has been a lifeline for many families and the national economy.
- Skill Acquisition: Many migrants gain valuable skills and experience abroad, which could potentially benefit Nepal if they return.
- International Networks: The Nepalese diaspora creates international connections that could be leveraged for the country’s development.
Looking Ahead: What Can Be Done?
Addressing this issue requires a multi-faceted approach. Here are some potential strategies:
- Skill Development: Align education and vocational training with both domestic and international market demands.
- Entrepreneurship Support: Create incubators and provide easier access to capital for young entrepreneurs.
- Foreign Investment: Improve the ease of doing business to attract foreign companies and create local job opportunities.
- Rural Development: Invest in rural infrastructure and promote agribusiness to make farming more attractive and profitable.
- Diaspora Engagement: Develop programs to engage the Nepalese diaspora in knowledge transfer and investment.
- Governance Reform: Address corruption and bureaucratic inefficiencies to create a more conducive environment for business and development.
- Tourism Hub: Improving existing infrastructure and promoting tourism at the international level to retain large population.
The Crossroads: Deciding Nepal’s Future
Nepal stands at a critical juncture. The decisions made in the coming years will shape the nation’s trajectory for decades. Will Nepal find a way to harness its demographic dividend, or will it face the prospect of a “lost generation”?
